Oct . 16, 2024 16:51 Back to list
Understanding Hepatitis C Testing Methods and Their Importance in Diagnosis
Understanding Hepatitis C Testing Importance, Methods, and Implications
Hepatitis C is a viral infection that primarily affects the liver, leading to both acute and chronic diseases. This condition is caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV), which can result in severe liver damage, cirrhosis, liver cancer, and even death if left untreated. Given its potential health implications, testing for hepatitis C is crucial for early detection, management, and treatment.
Why Testing is Important
The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that around 71 million people worldwide are living with chronic hepatitis C. Many individuals do not exhibit symptoms until the disease has progressed significantly, often making them unaware of their infection status. This is why hepatitis C testing is essential—it allows for early diagnosis, which is paramount for effective intervention.
Additionally, understanding one’s hepatitis C status can prevent the transmission of the virus to others. HCV is primarily spread through blood-to-blood contact. High-risk activities—such as sharing needles among drug users, receiving unscreened blood transfusions, or unsafely handling medical equipment—can contribute to its spread. By knowing their status, individuals can adopt safer practices and take necessary precautions to protect others.
Types of Hepatitis C Tests
Hepatitis C testing typically involves two main types of tests antibody tests and viral tests.
1. Antibody Tests The first step in assessing hepatitis C infection is the antibody test. This test checks for the presence of antibodies to HCV in the blood. If the result is positive, it indicates that a person has been exposed to the virus at some point. However, it does not differentiate between a current or past infection. Therefore, a positive antibody test may lead to further testing.
hepatitis c test s
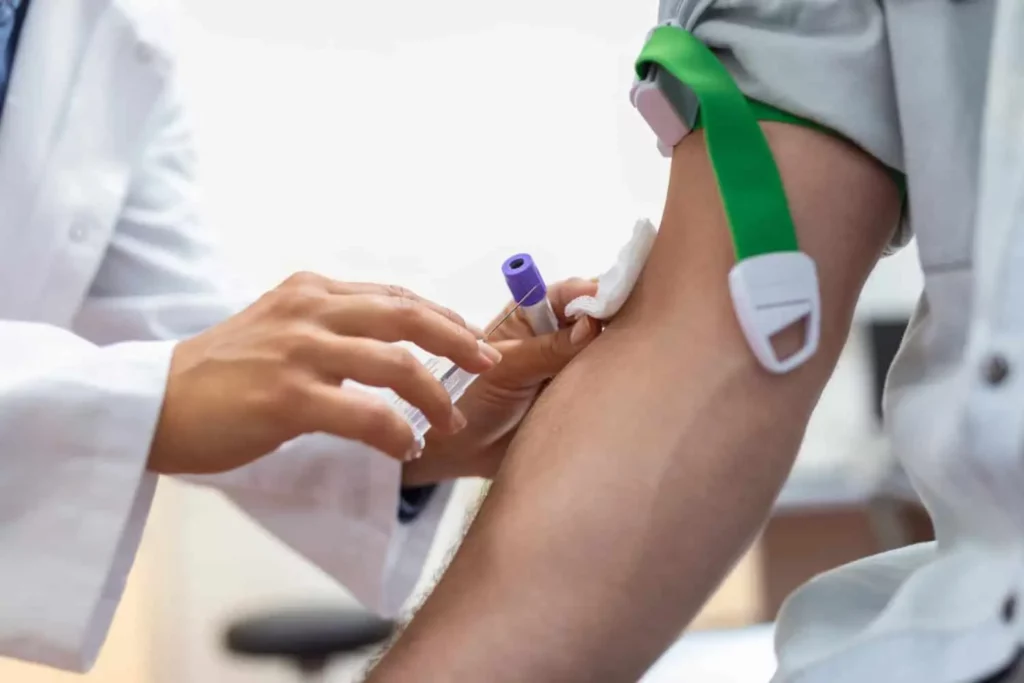
2. Viral Tests If the antibody test is positive, the next step usually involves a viral test, specifically a Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) test. This test detects the actual virus in the blood, determining whether someone is currently infected with hepatitis C. It can also measure the amount of virus, known as the viral load, which helps assess the severity of the infection.
In addition to these basic tests, genotyping tests can determine the specific strain of the virus, which helps guide treatment decisions based on how it reacts to various therapies.
Implications of Testing
Receiving a positive hepatitis C test result can be daunting. However, it is crucial to understand that hepatitis C is a treatable and manageable condition. Advances in medical science have led to the development of highly effective antiviral treatments that can cure the infection in approximately 95% of cases.
For those diagnosed with chronic hepatitis C, it is important to engage with healthcare providers for a comprehensive treatment plan. This may include lifestyle changes, regular monitoring of liver health, and, in many cases, direct-acting antiviral (DAA) therapy. These medications have transformed hepatitis C treatment, often requiring only 8 to 12 weeks of therapy with minimal side effects.
Conclusion
The importance of hepatitis C testing cannot be overstated. Early detection plays a critical role in preventing long-term health complications associated with the virus and helps curb the epidemic by reducing transmission rates. As awareness about hepatitis C grows, so does the imperative for individuals, especially those at higher risk, to undergo regular testing.
Maintaining open conversations about hepatitis C, its testing, and treatment options can significantly affect the overall health of communities. By prioritizing education and awareness about hepatitis C, we can foster a more informed society that encourages testing and ultimately leads to better health outcomes for all. Whether through awareness campaigns, community health initiatives, or routine healthcare check-ups, emphasizing the need for hepatitis C testing is essential in the ongoing battle against this pervasive infection.
-
Accurate Benzodiazepines (BZO) Rapid Test Kits | Fast Results
NewsAug.27,2025
-
Trusted Early Pregnancy Test Kit Supplier | Accurate, Fast Results
NewsAug.26,2025
-
China Sterile Nylon Flocked Throat Swabs: Superior Sample Collection
NewsAug.25,2025
-
COVID-19 Rapid Antigen Test Kit: Accurate & Fast Home Results
NewsAug.24,2025
-
Premium Cassette Lateral Flow Devices for Rapid Diagnostics
NewsAug.23,2025
-
Pregnancy Test Calculator: Know Your Weeks, Week by Week
NewsAug.22,2025

