Nov . 19, 2024 02:08 Back to list
COVID-19 Fast Testing Kit for Quick and Efficient Results at Home
Understanding COVID-19 Rapid Test Kits A Guide
The COVID-19 pandemic has dramatically altered our daily lives, pushing governments, health organizations, and researchers to innovate solutions for testing and controlling the virus. Among the numerous tools developed to combat the spread of the virus, COVID-19 rapid test kits have emerged as a pivotal component in public health strategy. These kits provide fast and accessible testing options that have been crucial for early detection and immediate response efforts.
What Are COVID-19 Rapid Test Kits?
COVID-19 rapid test kits are diagnostic tools designed to determine if an individual is currently infected with the virus responsible for COVID-19, known as SARS-CoV-2. Unlike traditional PCR (polymerase chain reaction) tests, which can take hours or even days to yield results, rapid tests can provide results within 15 to 30 minutes. This quick turnaround makes them invaluable, especially in settings like schools, workplaces, and large gatherings where immediate results can influence ongoing activities.
There are two main types of rapid tests antigen tests and antibody tests
.1. Antigen Tests These tests detect proteins from the virus itself. They are generally used for diagnosing active infections. A sample is typically obtained through a nasal swab, and the test can indicate the presence of the virus quickly. However, antigen tests may not be as sensitive as PCR tests, particularly in individuals with low viral loads.
2. Antibody Tests Unlike antigen tests, these are used to determine if someone has previously been infected with COVID-19 by detecting antibodies in the bloodstream. Antibody tests, while useful in understanding population immunity and epidemiology of the disease, are not designed for diagnosing active infections.
Advantages of Rapid Test Kits
The primary advantage of rapid test kits lies in their speed and ease of use. They can be employed in a variety of settings, including remote locations, providing invaluable feedback quickly. This capability allows for immediate isolation of positive cases and helps limit further transmission of the virus.
Additionally, rapid testing enhances surveillance efforts. Public health officials can deploy these tests in community settings to monitor outbreaks and inform decision-making on public safety measures. The simplicity of the testing process makes it possible for non-laboratory professionals to administer the tests, further increasing accessibility.
covid rapid test kit
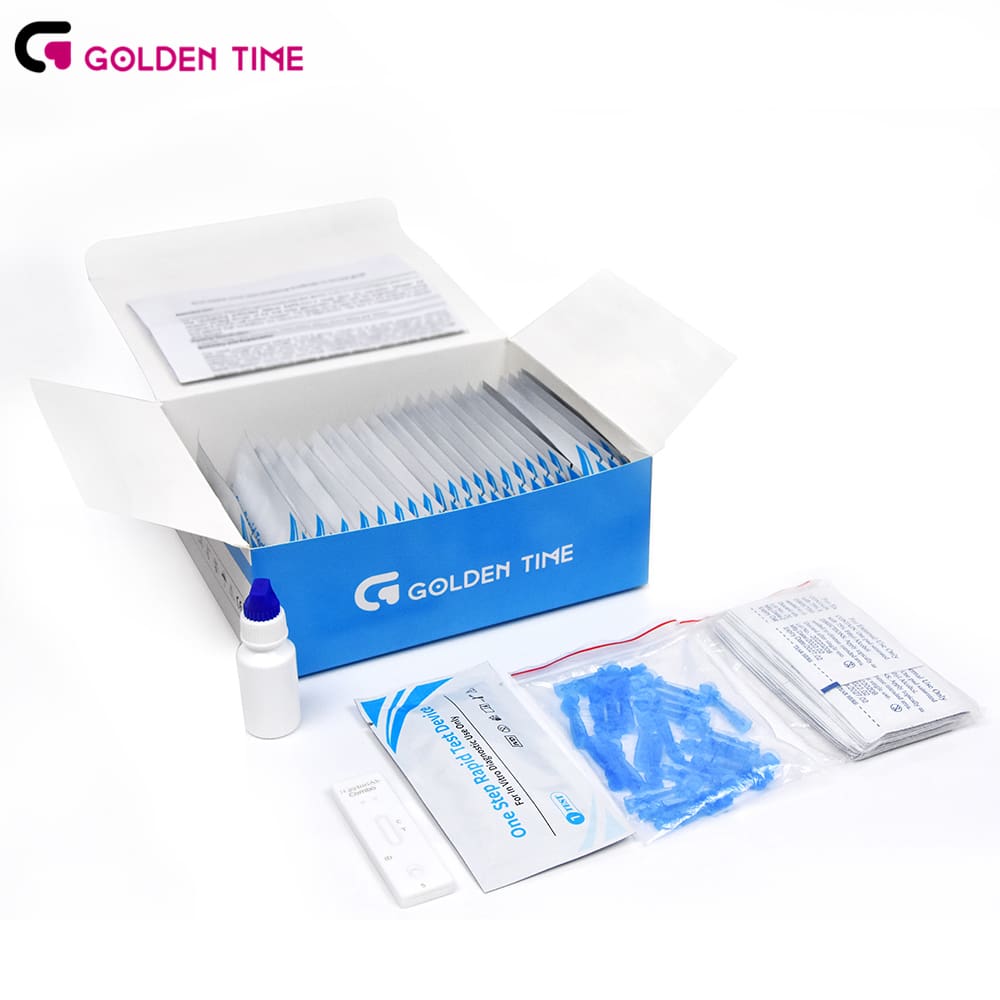
Rapid tests can also foster greater participation in testing programs. The convenience of receiving results within minutes encourages individuals to get tested more regularly, especially if they are symptomatic or have been exposed to confirmed cases.
Limitations and Considerations
Despite their benefits, rapid test kits come with certain limitations. For instance, the accuracy of rapid antigen tests can be lower than that of PCR tests, particularly in asymptomatic individuals or those early in their infection. This can lead to false negatives, which poses a risk of unknowingly spreading the virus.
Additionally, the quality of the rapid test kits can vary significantly. Not all tests are created equal, and it is essential for users to select tests that are authorized by health authorities, such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) or the World Health Organization (WHO).
Another consideration is the need for follow-up testing. If a rapid test yields a negative result but symptoms persist or exposure is known, a confirmatory PCR test may still be necessary to rule out infection conclusively.
The Future of COVID-19 Rapid Testing
As the pandemic evolves, so too will testing technologies. Scientists are continually refining rapid test kits to enhance their accuracy, reliability, and ease of use. The goal is to create tests that are not only quick but also provide highly accurate results comparable to those of laboratory methods.
In the aftermath of the COVID-19 pandemic, the importance of rapid testing is likely to extend beyond this crisis. Enhanced rapid testing capabilities may become standard practice in managing and controlling infectious diseases, presenting an effective tool in public health arsenal for future outbreaks.
In conclusion, COVID-19 rapid test kits represent a significant advancement in our ability to respond quickly to viral outbreaks. Their speed and accessibility can play a crucial role in identifying and isolating cases to control the spread of COVID-19, while ongoing improvements may further enhance their efficacy in public health strategies moving forward. As the world adapts to the ongoing challenges posed by COVID-19, these testing kits will undoubtedly remain a focal point in health and safety discussions.
-
Malaria Pf Ag Rapid Test Kit - Quick & Accurate Detection
NewsAug.11,2025
-
Accurate Cardiac Marker CK-MB Rapid Test for Quick Results
NewsAug.10,2025
-
Premium Empty ABS Plastic Cassette for Test Strips
NewsAug.09,2025
-
Sterile Urine Cup: Accurate Specimen Collection for Labs & Home
NewsAug.08,2025
-
Malaria Pf/Pan Ag Rapid Test Kit for Fast, Accurate Diagnosis
NewsAug.07,2025
-
Rapid Canine Corona Test: Fast & Accurate Results
NewsAug.06,2025

